Factsheet - Quality publication of datasets
Introduction
This information sheet has been drawn up to help you publish quality datasets, making it easier to re-use the data, especially in the context of an open data initiative.
Data quality is essential to ensure its usefulness and impact. Here are the 3 key steps and best practices for ensuring that your data meets quality standards.
Assess the quality of a dataset
= Clean, structure and format data to ensure its accuracy and usefulness.
- Ensuring that the data is correct
- Ensuring that data sets are complete
The data must be exhaustive, within the limits of the legal constraints relating to the protection of personal data.
- Ensure that the data is structured (e.g. one column per variable)
- Try to publish primary data
This is data collected directly from the source, not aggregated, and provided at the highest possible level of granularity.
Prepare a quality dataset
= Provide detailed descriptions, metadata and instructions for use to make the data understandable and easy to use.
This involves structuring the data:
- Make sure you use clear headings: an explicit and concise title
- Make sure you provide a description of the content, and possibly even a description of the source and method of data collection.
Example:

- Make sure to add relevant keywords to facilitate the search (several languages are possible)
Example:
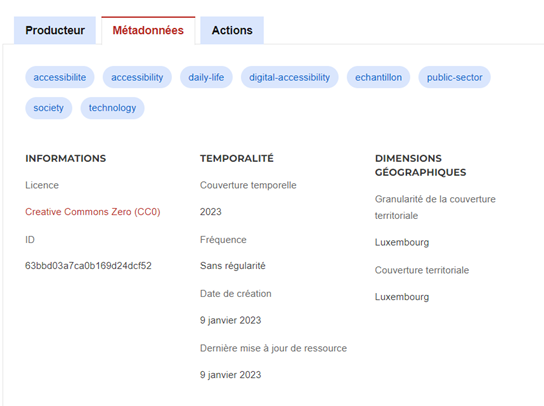
- Make sure to specify the licence under which the data is published (for example, Creative Commons). Government policy recommends choosing the CC-0 licence.
Data must be provided in open and reusable formats. For example, the PDF format is not considered reusable because it cannot be directly integrated into software for further processing. For Luxembourg, application of the Creative Commons family of licences is strongly recommended, with a clear preference for the Creative Commons Zero CC0 licence: this is the "no copyright reserved" option in the Creative Commons toolkit, which effectively means relinquishing all copyright and similar rights you hold in a work and assigning these rights to the public domain.
To find out more, see our Open data fact sheet on using licences.
Data format:
- Make sure you use open and widely accepted formats (for example; CSV, JSON, XML,...) Avoid PDFs which make re-use difficult. For geospatial data, use formats such as (for example; GeoJSON, KML, Shapefile,...).
Improve the quality of a dataset on an ongoing basis
= Implement regular review and update processes to maintain data relevance and accuracy.
- Ensure that data is regularly updated
Data must be current, ideally in real time, to maximise its relevance. One way of achieving this is to consider periodic data reviews. This will ensure the continuity of the data flow and therefore its relevance.
- Maintain an open communication channel for feedback and updates.
Get involved with users, whether citizens, businesses or developers, as often as possible. This will ensure that the next iteration of the service is as relevant as possible. It is essential to bear in mind that much of the data will not reach end users directly, but rather through people who use the data and transform or remix it to present it to others.
- Bonus: don't hesitate to use social networks or other channels to promote your data sets.
- Bonus: don't hesitate to collaborate with other organisations to extend the reach of the data.
Conclusion
By following these guidelines, you will contribute to the creation and maintenance of high-quality datasets on data.public.lu. Well prepared and documented data is essential to support research, innovation and transparency in Luxembourg.
For more information, please consult the following pages:
